Beating the Heat: The Renewable Resources and Technologies Preventing Power Outages
- Written by Amy Opheim
- June 27, 2024

It’s hot out there! More than 100 million Americans were under heat advisory warnings last month, as record-breaking temperatures scorched the East Coast and Midwest. Yet even with AC and fans running full blast across the country, the power grid held up surprisingly well, and is predicted to hold throughout the summer, despite forecasted high temps. This contrasts with summers past, when increased demand for cooling systems, heat-induced strains on power generating equipment, overheated power transmission lines, and other heat-related issues forced rolling blackouts and caused disruptive and extended outages.
So, what’s different this year? 2023 was a record-breaking year for clean energy, with a full 25% of electricity generated in the U.S. coming from renewable sources in the first half of the year. Solar was the largest growth driver, with a 55% increase in solar energy capacity installation last year; in fact, each of the country’s power grids set solar generation records last summer. Last year also saw a substantial increase in battery storage capacity, which is expected to double again in 2024.
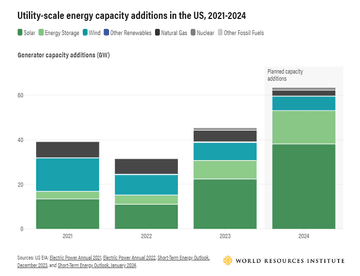
Despite operating at full or close-to-full capacity during last month’s heat waves, this increase in renewable energy is enabling the country’s power grids to withstand the drastic increase in demand. During last year’s heatwave, many grid operators set records for the percent of renewables serving their energy loads.
Enhancements in grid technology are also playing a critical role in protecting the grid during extreme weather, such as heat waves. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) collects energy usage data, enabling utilities to monitor real time usage and develop effective demand response programs. Smart grids enable energy providers to manage supply and demand in real time, monitoring power flow to match energy generation. They utilize Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) to help balance supply and demand, seamlessly integrating renewable and traditional power sources. Additionally, smart grids incorporate vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, allowing EV users to share electricity stored in their vehicles' batteries with the grid during peak times. Automated smart grid networks can also accept power from various customer batteries, creating virtual power plants that pool, store, and deploy extra power during peak usage periods and outages.
To keep pace with extreme weather phenomena, including global warming, energy provider portfolios should include both renewable energy sources and the smart grid technology necessary to successfully measure, manage, and deploy a variety of power sources in typical and extreme conditions. Resource Innovations supports utilities across the country with industry-leading expertise in energy efficiency programs, demand side management, renewable energy integration, and more. Contact us today to talk about incorporating smart grid technologies.
Related Resources
Explore Resource Innovations' grid insights.